Closed System in Thermodynamics
The first law of thermodynamics is generally thought to be the least demanding to grasp as it is an extension of the law of conservation of energy meaning that energy can be neither created nor destroyed. Bahman Zohuri in Physics of Cryogenics 2018.

Timeline Photos Mechanical Engineers Rocks Facebook Energy System Thermodynamics Mechanical Engineering
The first law specifies that energy can be transferred between physical systems as heat as work and with transfer of matter.
. We say the state of a system is an equilibrium state if the macroscopic variables that characterise the system do not change in time. The term equilibrium in thermodynamics appears in a different context. By putting a lid on the saucepan the matter can no longer transfer because the lid prevents the matter from entering the saucepan and leaving the saucepan-This example you will understand when you read open system examples.
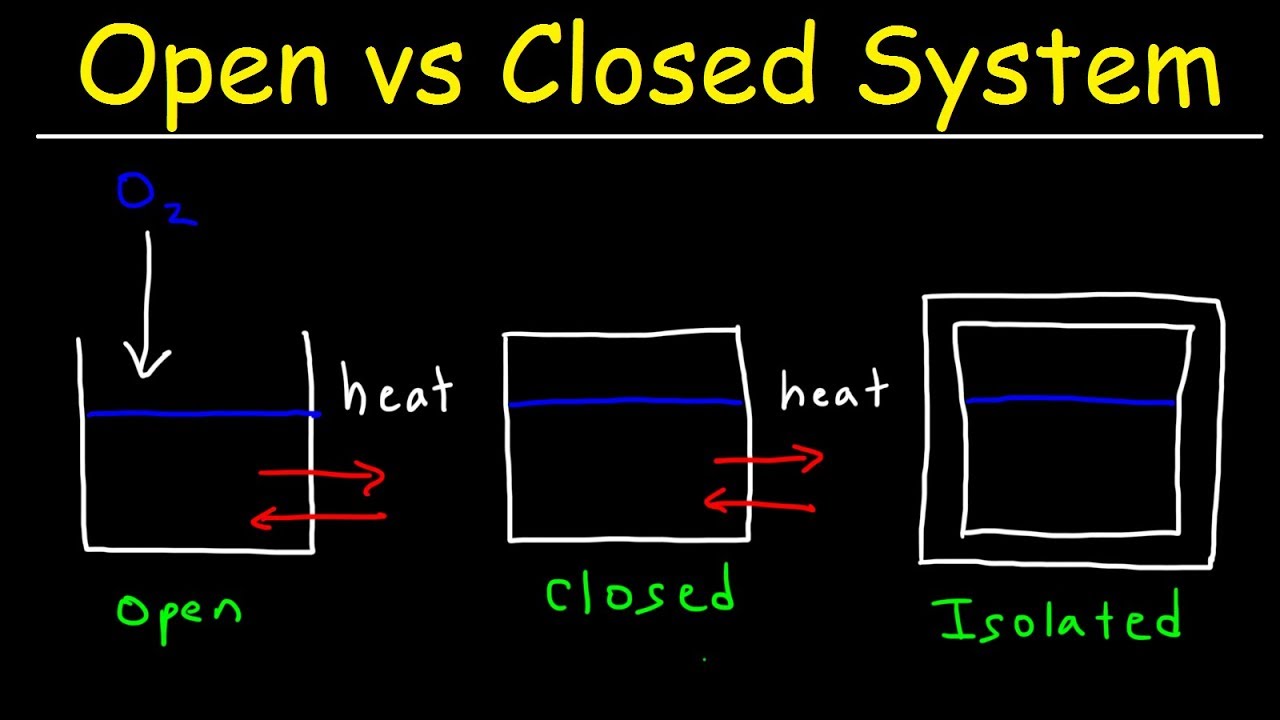
Thermodynamics defines a system as the part of the universe under study that is the part where observations are made. Rosen in Exergy Third Edition 2021. One way to generalize the example is to consider the heat engine and its heat reservoir as parts of an isolated or closed systemie one that does not exchange heat or work with its surroundings.
Thermodynamics Chemistry Chapter 6 Important Terms and Definitions System. Refers to the portion of universe which is under observation. Putting a lid on the saucepan makes the saucepan a closed system.
The first law of thermodynamics is the law of the conservation of energy which states that although energy can change form it can be neither be created nor destroyedThe FLT defines internal energy as a state function and provides a formal statement. External force and torque on a system are zero. Closed System Across the boundary of the closed system the transfer of energy takes place but the transfer of mass doesnt take place.
However much energy there was at the start of the universe there will be that amount at the end. 2 Flow work of fluid as it exits the system P pressure Ï specific volume P 1 Ï 1 Flow work of fluid as it enters the system dE. The presence of reactants in a closed vessel made of conducting material eg copper or steel is an example of a closed system.
The closed-loop system is defined as Feedback from the output to the input is missing in the open-loop control system. A closed system is referred to the system where only energy can be. The law of conservation of energy states that.
Work done by a system is positive and the work done on a system is. 124 The first law of thermodynamics FLT. The example of a heat engine illustrates one of the many ways in which the second law of thermodynamics can be applied.
This is one definition used for the arrow of time since entropy of the universe will always increase over time according to the second law of thermodynamics. A description of any thermodynamic system employs the four laws of thermodynamics that form an axiomatic basis. Bahrami ENSC 388 F09 1 st Law of Thermodynamics.
So now Open system 2. A system is said to be a closed system when there is no exchange of matter but exchange of energy is possible. Closed Systems 3 w kJkg work per unit mass w kWkg power per unit mass Sign convention.
Mass is not fixed. Ibrahim Dincer Marc A. The second law defines the existence of a quantity called entropy that describes the direction.
For example a gas inside a closed rigid container completely insulated from its. To obtain More accurate Control the controlled variable should be fed back and compared with the reference input. The thermodynamic laws provide a quantitative description of these quantities.
Thermodynamics is a branch in physics that deals with the interconversion of heat and other forms of energy. In any closed system in other words each time a system goes through a thermodynamic process the system can never completely return to precisely the same state it was in before. The first law of thermodynamics is a version of the law of conservation of energy adapted for thermodynamic processes distinguishing three kinds of transfer of energy as heat as thermodynamic work and as energy associated with matter transfer and relating them to a function of a bodys state called internal energy.
Closed System In a closed system there is no exchange of matter but exchange of energy is possible between system and the surroundings Fig. Presence of reactants in an open beaker is an example of an open system. The surrounding and universe interact with each other and depending on the type of the system exchange of matter and energies occur.
For example the heat. 62 Open closed and isolated systems.

Open System Closed System And Isolated System Thermodynamics Physics

Open Vs Closed Vs Isolated Thermodynamic Systems Thermodynamics Internal Energy Free Energy

Open System Closed System Isolated System Details System Thermodynamics Mechanical Energy

Different Types Of Thermodynamic Systems Open System Closed System Isolated S Sponsored Paid Affiliate Thermodynamic Thermodynamics System Chemistry
No comments for "Closed System in Thermodynamics"
Post a Comment